A Guide to Self-Care: Reducing Anxiety Naturally
In the modern world, anxiety has become a commonplace term, yet not everyone fully grasps the complexity and intensity of this condition. We all experience anxiety in different forms and intensities. Whether it’s the generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, or any phobia-related disorders. For the unaware, symptoms of anxiety can be baffling and hence, a clear understanding is a step towards tackling this issue head on. Through this piece, you will gain an in-depth comprehension of what anxiety truly is, debunk the myths surrounding it, and delve into stress management techniques which can potentially alleviate the condition. Additionally, get acquainted with mindfulness and meditation exercises to help you gain control over your body and mind, and explore how nutrition, physical activities, and healthy sleeping habits can play vital roles in your battle against anxiety.
Understanding Anxiety
Anxiety, by definition, is a normal and often healthy emotion that generates feelings of fear or apprehension in response to stressful situations. However, when an individual experiences excessive, persistent, and irrational anxiety and worry about everyday situations for no definitive reasons, this may indicate a medical disorder known as anxiety disorder.
Anxiety disorders have various types, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and phobia-related disorders. Each type may exhibit different symptoms but they generally comprise feelings of restlessness, fatigue, difficulty in concentrating, and sleep-related problems.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
GAD is characterized by excessive worry about ordinary day-to-day activities. Individuals with GAD may find it hard to stop worrying about health, work, school, or money, and this anticipation of disaster interferes with their normal routine.
Panic Disorder

Panic Disorder features repeated and unpredictable episodes of intense fear. These panic attacks can come upon suddenly, peaking within minutes, and can bring about palpitations, sweating, trembling, and a feeling of impending doom.
Phobia-Related Disorders
Phobia-Related Disorders involve intense fear or aversion toward specific things or situations. Examples include agoraphobia (fear of being in situations where escape might be difficult) and social anxiety disorder (intense fear of being humiliated or observed in social or performance situations).
Effects of Anxiety on an Individual’s Life
Anxiety disorders can interfere with a person’s daily life, limiting their ability to function at work, school, and social environments. They may also lead to physical symptoms like headaches, muscle aches, stomach aches or fatigue. Anxiety disorders can foster a cycle of fear and worry, feeding the disorders and making them harder for the individual to overcome.
Effective Self-Care Techniques for Anxiety Management
Anxiety management involves a blend of physical, mental, and emotional strategies. Physical activity plays a crucial role; whether it’s yoga, regular exercise, or just a simple walk, it aids in reducing stress hormone production and promotes relaxation.
Adhering to a healthy diet full of fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains is also important as it fuels your brain and body adequately. Try reducing your caffeine and alcohol intake, both of which can potentially trigger or amplify anxiety symptoms.
Mindfulness and meditation practices help you stay grounded in the present, thereby helping in managing anxious thoughts. Techniques to shift negative thoughts towards positive or neutral ones can lead to a healthier mindset. Moreover, relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or visualization can aid in alleviating anxiety symptoms.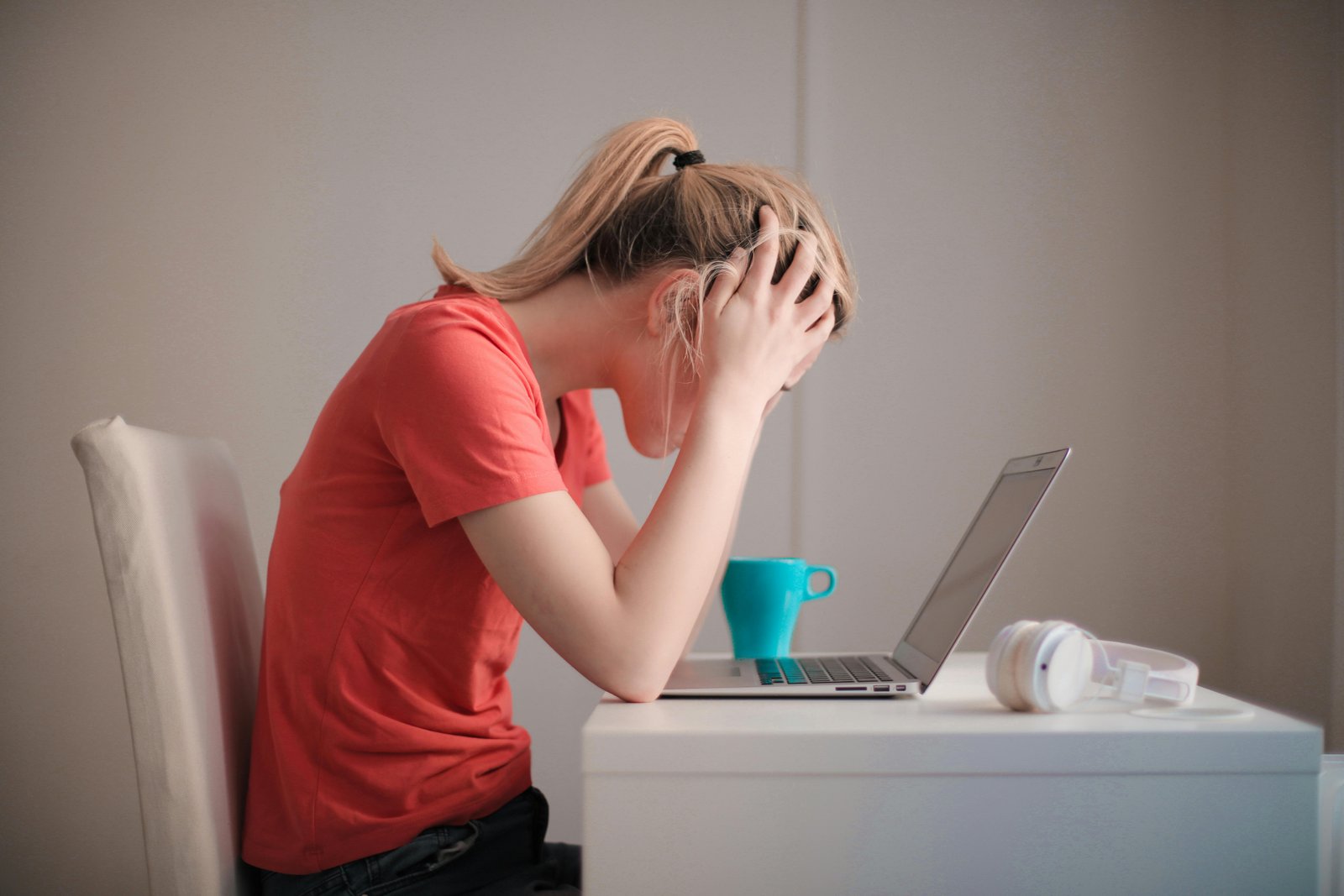
Never overlook the importance of a good night’s sleep in dealing with anxiety, as insufficient sleep can escalate anxious thoughts and feelings. Regular sleep pattern and a serene sleep environment can encourage better sleep.
Discussing your feelings with a trusted friend, family member, mentor, or counselor can be enormously therapeutic. Verbalizing your concerns can often lighten the burden of your worries. And do not hesitate to seek professional help in managing anxiety. After all, mental health is as important as physical health, and caring for it helps you lead a balanced, fulfilled life.
Understanding the Connection Between Stress and Anxiety
Anxiety is often brought on by prolonged periods of high stress. It’s completely natural to experience stress in response to challenging or unfavorable situations. However, when it becomes chronic and starts interfering with your daily life, it can evolve into anxiety disorders. Hence, stress management forms an integral part of the self-care regime for individuals coping with anxiety.
Applying Time Management Skills
One of the effective ways to manage stress and, in turn, reduce anxiety is to improve your time management skills. Effective time management helps to maintain balance, prevent burnout, and increase productivity, ultimately reducing feelings of stress and overwhelm. Using a schedule or calendar, creating a to-do list, and taking regular breaks are some examples of essential time management techniques.
Prioritizing Tasks
To support time management skills, it’s crucial to learn the art of prioritizing tasks. This process involves determining the importance and urgency of tasks and arranging them to be handled in priority order. It’s useful to focus on high-priority tasks first. Doing so can help you avoid feeling overwhelmed and manage stress more effectively. It also allows you to focus your attention on one thing at a time, a mindfulness practice that can also help manage feelings of anxiety.
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting realistic goals is another critical self-care strategy for individuals with anxiety. It is important to have aspirations but equally necessary to set attainable and well-delineated goals in order to lessen the likelihood of becoming overwhelmed, which can result in heightened anxiety. Breaking down extensive projects or tasks into smaller, more manageable components can make the overall goal seem less daunting.
Less Stress Lifestyle
Living a lifestyle focused on reducing stress can be beneficial in managing anxiety. Such a lifestyle can incorporate regular physical activity, adequate sleep, nutritious diet, and incorporating relaxation and leisure activities. Mindfulness and relaxation techniques, like deep breathing, guided imagery, meditation, and yoga, can help decrease the level of stress hormones in the body and promote feelings of calm and wellness.
Recognizing and Identifying Stressors
Recognizing and identifying stressors are also an essential part of stress management. Stressors are specific events or worries that cause stress. Once identified, these can be effectively managed or mitigated to reduce the intensity of stress. This may involve problem-solving strategies, healthy coping mechanisms, or professional help for more complex stressors.
Considering Professional Consultation
It’s vital to acknowledge that persistent stress and anxiety may necessitate professional intervention, despite our best self-care routines. Those trained in mental health fields, like psychologists or therapists, have a wealth of guidance and coping strategies to offer. Methods such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, or dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) serve as vital resources to alleviate and manage anxiety symptoms.
Mindfulness and Meditation
The Power of Mindfulness and Meditation
Simultaneously, exploring mindfulness and meditation provides another avenue for easing anxiety. Essentially, mindfulness is the practice of remaining fully conscious and absorbed in the present moment. On the other hand, meditation trains your attention and awareness to promote mental clarity and emotional calmness. These tools blend well with professional treatments, reinforcing their effects and providing additional control over anxiety.
How Mindfulness and Meditation work
Mindfulness and meditation work by allowing us to focus on the present moment, rather than being overwhelmed by our thoughts or anxieties. This can help create a sense of calm and relaxation, reducing feelings of stress and worry. With practice, these techniques can help us develop a more compassionate, non-judgmental attitude towards ourselves and our experiences.
Benefits of Mindfulness and Meditation
There are multiple benefits that stem from mindfulness and meditation practices. For instance, they can help to reduce stress, calm the mind, improve attention, and enhance overall well-being. Specifically related to anxiety, these practices can help individuals recognize their anxiety triggers, understand their emotions, and respond more effectively to stressful situations. They can provide a sense of mental and emotional balance, fostering healthier coping mechanisms.
Incorporating Mindfulness and Meditation into Daily Life
Incorporating mindfulness and meditation into daily life doesn’t necessarily mean spending hours at a time meditating. Even just a few minutes a day can make a significant difference. It can be as simple as starting the day with a few minutes of quiet reflection, incorporating mindful breathing exercises during a midday break, or ending the day with a guided meditation to ease into sleep.
Mindfulness can also be incorporated into routine activities like eating, walking, or chores around the house. It involves intentionally paying attention to the sensations, emotions, and thoughts that arise during these activities.
Guided Meditation and Anxiety
For those new to the practice or who struggle with focusing during meditation, guided meditation may be a beneficial starting point. Guided meditation involves a narrator or teacher guiding you through a meditation, often using visualization or other techniques to help you relax and calm your mind.
You can find guided meditations in various lengths, from just a few minutes to longer sessions, which can be tailored to individual needs and schedules.
Utilizing Mindful Breathing and Yoga Techniques
Managing anxiety can often be accomplished through the use of mindful breathing, also known as diaphragmatic or deep breathing. This technique promotes relaxation and calmness by encouraging individuals to breathe deeply, thereby allowing the stomach (rather than the chest) to rise with each intake of breath. Concentrating on and intentionally controlling one’s breathing can lead to a greater sense of tranquility.
In addition to mindful breathing, yoga is another effective practice for coping with anxiety. Incorporating physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation, yoga provides both physical and psychological benefits. By cultivating mindfulness, yoga enables individuals to gain a heightened awareness of their mental and physical states.
Debunking Myths about Anxiety
Addressing Myths: Anxiety Is More Than Just Overthinking
A prevalent myth is that anxiety is merely a result of overthinking, and people can relieve it by disregarding certain thoughts. This misconception trivializes anxiety, a complex condition that combines extreme worry with physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, nausea, and lightheadedness. Controlling anxiety is not as easy as it is often perceived.
A crucial part of self-care for anxiety involves recognizing it as a genuine condition that is multi-dimensional in nature. Understanding that seeking professional help or using medication isn’t a sign of weakness but a proactive approach to handling your mental health is also fundamental.
Myth 2: Anxiety Isn’t a Real Illness
Society often labels anxiety as a personality flaw or character trait rather than recognizing it as a legitimate medical condition. The reality is that anxiety is a clinical disorder that can have a significant impact on quality of life. It can result from a combination of genetic factors, brain chemistry, and life experiences such as trauma or stress.
Regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, and cutting down on caffeine and alcohol can help manage anxiety symptoms. Remember, seeking medical help is just as important when you’re dealing with mental health problems as it is for physical health issues.
Myth 3: Medication is the Only Solution
While medication can indeed help people struggling with anxiety, it’s not the only solution. Several other therapies can be just as effective, like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness, and other relaxation techniques.
Self-care techniques for anxiety may include practices such as deep breathing, yoga, and meditation. These can help you stay grounded and centered, reducing anxiety symptoms. Research has shown that regular mindfulness practice can significantly reduce stress and symptoms of anxiety.
Myth 4: Everyone’s Anxiety is the Same
Just like no two people are entirely alike, anxiety symptoms and triggers can significantly vary from person to person. One person’s experience with anxiety might look entirely different from another’s. Therefore, self-care and treatment plans should be customized to suit each individual’s needs.
To manage this, maintain a journal to identify your triggers and understand your symptoms better. This can help create a personalized self-care plan to effectively manage your anxiety.
Dispelling Myth 5: Anxiety Isn’t Something You Can Just Snap Out Of
One commonly held misconception is the assumption that individuals suffering from anxiety can simply “snap out of it”. This could not be further from the truth. The journey to overcoming anxiety involves reasoning, managing behaviors, and often, the need for professional intervention.
As part of your self-care regimen, it is important to set aside time for relaxation techniques, carry out regular self-check-ins to monitor your mental state and do not hesitate to reach out for professional support when necessary. Remember, it’s perfectly fine not to be okay at all times, and seeking help is a key step when required.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Emphasizing Nutrition: A Key Element In Anxiety Management
The role that nutrition plays in mental health, especially in dealing with anxiety, can’t be overstated. Maintaining a balanced diet can help modulate mood, decrease symptoms of anxiety, and foster overall well-being. Sources of vitamin B such as whole grains, meat, eggs, and legumes are beneficial as they aid the body in mood regulation and are known to help alleviate anxiety. Omega-3 fatty acids common in seafood, for example, salmon, can bolster brain health and help to lower stress levels. By incorporating magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, and seeds in your diet, you can significantly enhance the brain’s ability to resist stress.
Avoiding Harmful Substances
Avoiding substances like caffeine and alcohol is also advised because these substances can trigger anxiety and panic attacks. Caffeine, a stimulant, can increase feelings of nervousness and jitteriness. Alcohol, on the other hand, can disrupt sleep patterns and potentially heighten anxiety during periods of withdrawal.
Physical Activity and Anxiety Reduction
Physical activity can be an effective way to manage anxiety. Studies have shown that regular physical activity can reduce symptoms of anxiety by improving mood and acting as a natural stress reducer. Physical activity stimulates the production of endorphins, the body’s natural mood elevators. This doesn’t mean you have to start running marathons — gentle exercises like yoga and pilates or even taking a daily walk can significantly help manage anxiety levels.
The Significance of Adequate Sleep
People dealing with anxiety often have trouble with sleep, but getting a good night’s sleep is incredibly important for mental health. Sleep deprivation not only exacerbates anxiety symptoms but it can also trigger new episodes. Therefore, developing healthy sleep habits is an important aspect of managing anxiety. To improve sleep hygiene: make your sleep environment as comfortable as possible, including using a high quality mattress and pillows, maintaining a cool room temperature, and blocking out all light sources. It is also critical to establish a regular sleep schedule where you go to bed and wake up at the same time each day.
Holistic Lifestyle Changes for Anxiety Management
Incorporating changes into your everyday routine can tremendously help with anxiety management. Creating a healthy routine that includes adequate sleep, regular physical activity, balanced meals, and dedicates time for relaxation can lead to improved mental health. It’s also beneficial to incorporate activities you enjoy into your routine to help distract and refocus your mind from anxiety-provoking thoughts. Regular meditation or mindfulness exercises can also aid in anxiety management, with numerous studies demonstrating an ability to reduce anxiety and promote a sense of calm.
Need for Professional Support
While diet, exercise, and sleep can be effective in managing anxiety, it’s also vital to note that professional help may be necessary. Relying solely on self-care for serious anxiety disorder can be ineffective. If your anxiety is overwhelming or debilitating, seeking help from a mental health professional is crucial.
Establishing New Habits: A Journey, Not a Sprint
When embarking on the endeavor to change your lifestyle habits as a means to manage anxiety, remember that it’s a gradual process that requires patience. It is unlikely you’ll see immediate improvements, but that is completely normal. The true key to managing anxiety effectively lies within small, consistent steps. Make sure to acknowledge and celebrate even the smallest of victories and advances. Most importantly, don’t let yourself be discouraged if you don’t notice improvements instantly.
Seeking Professional Help
Professional Assistance As a Part of Anxiety Self-Care
Self-care strategies are indeed instrumental in coping with anxiety, but they are not a substitute for professional intervention when the need arises. There are mental health professionals, such as psychologists, psychiatrists, and therapists, who are specifically trained to diagnose and provide treatment for anxiety disorders. They can offer a plethora of therapeutic strategies and methodologies tailor-designed for you.
Recognizing When to Seek Professional Help
The threshold for seeking professional help can vary from person to person as the experience of anxiety is subjective. However, there are certain signs that indicate when it’s time to consult a professional –
- Intensity: If your level of anxiety is consistently high and interferes with your ability to function or enjoy life.
- Frequency: If your feelings of anxiety are persistent or occur without a known cause.
- Physical Symptoms: If you experience physical symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness.
- Dependency: If you rely on substances such as alcohol or drugs to relieve your anxiety.
- Harmful Thought: If you’re having thoughts of self-harm or suicide.
How to Seek Help from Mental Health Professionals
When you decide to seek help, the first step is usually to speak with your primary care physician. They can refer you to a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, assess your symptoms, or provide initial treatment.
There are also a number of ways to seek help directly from mental health professionals. If you have health insurance, check the provider directory or call the customer service number on the back of your insurance card to find a provider who is covered. If you don’t have insurance, many communities have free or low-cost mental health clinics that can provide help. There are also online platforms that connect users with licensed counselors.
When you reach out to a mental health professional, they will typically have an initial consultation to understand your symptoms. Based on this evaluation, they can recommend a course of treatment that could include therapy, medication, or a combination of the two.
Types of Therapy for Anxiety
Depending on your personal situation and type of anxiety, different therapeutic techniques may be used. Here are a few examples of therapies that are commonly used to treat anxiety:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps explore the relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, aiming to restructure negative thought patterns that contribute to anxiety.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT focuses on mindfulness, emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness, teaching new skills to handle emotional situations.
- Exposure Therapy: In exposure therapy, you are gradually exposed to anxiety-causing situations in a safe and controlled environment to help manage and reduce fear.
In conclusion, while practicing self care is a crucial aspect of managing anxiety, it’s important to recognize when professional help is needed. Mental health professionals can provide qualified support and treatment, and seeking their help is a sign of strength and self-care.
While self-help techniques and practices form an instrumental part in managing anxiety, it’s essential to remember that they are not substitutable for professional help. If you, or someone you know, are experiencing symptoms of anxiety, reaching out to mental health professionals can create a significant difference. It’s their training, coupled with your efforts, that can lead to a healthier, happier you. Don’t hesitate to seek help when needed. After all, taking care of mental health is just as crucial as physical health. Anxiety, as overwheliming as it may seem, doesn’t have to define your life. You can take control, one day at a time, and remember, you’re not alone in this journey.





