5 Amazing Benefits of Bee Pollen Uses
Bee pollen, often referred to as nature’s superfood, has been used for centuries due to its various health benefits. This article will provide an in-depth look at bee pollen, exploring its properties, uses, and potential side effects. By the end, you’ll understand why bee pollen can be a valuable addition to your diet.
Understanding Bee Pollen: A Comprehensive Overview
Bee pollen is a mixture of flower pollen, nectar, enzymes, honey, and wax that bees collect and store in their hives. It is often referred to as “bee bread” and serves as a primary food source for the bees. However, humans can also benefit greatly from its nutrient-rich composition.
Bee pollen is not only a natural treasure for bees, but it also offers a treasure trove of health benefits for humans. The concentrated source of vitamins, minerals, proteins, and antioxidants found in bee pollen makes it a valuable addition to any diet. Its diverse nutrient profile includes essential B vitamins, such as thiamin, riboflavin, and niacin, which play a crucial role in energy production and metabolism. Additionally, bee pollen contains vitamin C, an important antioxidant that supports immune function and collagen synthesis.
Furthermore, bee pollen is a rich source of vitamin E, a potent antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative damage. This vitamin is also known for its skin-nourishing properties, promoting a healthy complexion and reducing the signs of aging. The presence of potassium, calcium, and magnesium in bee pollen contributes to its mineral content, supporting healthy bones, muscles, and nerve function.

In addition to vitamins and minerals, bee pollen is packed with phytonutrients, which are natural compounds found in plants that have been shown to have numerous health benefits. These phytonutrients act as antioxidants, helping to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Bee pollen also contains enzymes that aid in digestion and promote optimal nutrient absorption.
What is Bee Pollen?
Bee pollen is essentially a concentrated source of vitamins, minerals, proteins, and antioxidants. It contains a wide array of nutrients, including B vitamins, vitamin C, vitamin E, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. Furthermore, it is rich in phytonutrients, enzymes, and beneficial fatty acids.
When bees collect pollen from flowers, they mix it with nectar and enzymes secreted from their salivary glands. This mixture is then stored in specialized structures on their hind legs called pollen baskets. As bees fly from flower to flower, they transfer pollen from the male part of the flower (the stamen) to the female part (the pistil), facilitating the process of pollination. In the process, they inadvertently collect pollen on their bodies, which they then groom and pack into the pollen baskets.
Once back at the hive, bees unload the pollen from their pollen baskets into storage cells. They mix it with honey and enzymes, which begin the process of fermentation. This fermentation process breaks down the complex sugars in the nectar and pollen, making it easier for the bees to digest and store for later use. The resulting mixture, known as bee bread or bee pollen, becomes a vital source of nutrition for the entire bee colony.
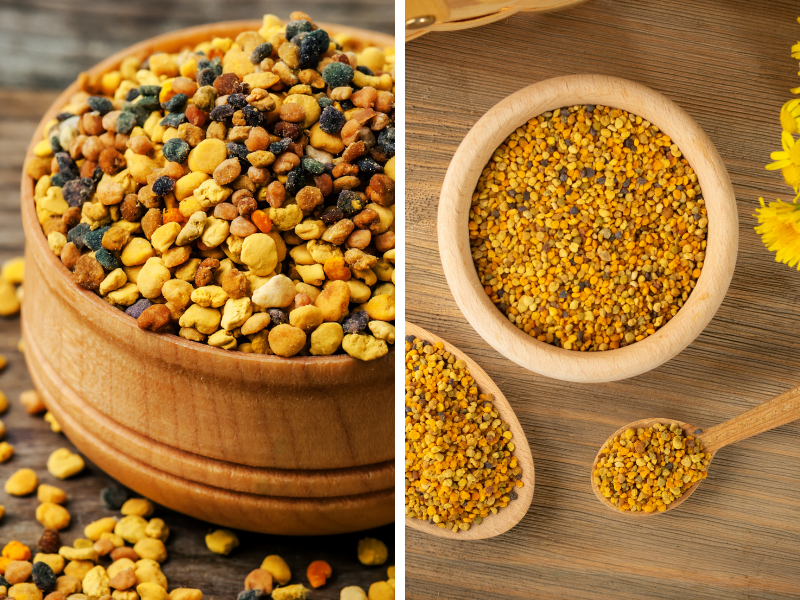

How is Bee Pollen Collected?
Beekeepers harvest bee pollen by placing special traps at the entrance of the hive. These traps are designed in a way that allows bees to enter the hive but causes them to brush against the trap, dislodging the pollen from their legs. The dislodged pollen then falls into a collection tray, where it is carefully collected by the beekeeper.
Once the bee pollen is collected, it undergoes a meticulous cleaning process to remove any impurities, such as dirt, debris, or bee parts. This ensures that the final product is pure and safe for consumption. After cleaning, the bee pollen is carefully dried to preserve its nutritional content and prevent spoilage. Finally, it is packaged in airtight containers to maintain its freshness and ensure a longer shelf life.
It is important to note that bee pollen can vary in color, taste, and texture depending on the plants from which the bees collected it. The color can range from yellow to dark brown, while the taste can be slightly sweet or slightly bitter. The texture can be powdery or granular, depending on the drying process and the size of the pollen grains.
When purchasing bee pollen, it is advisable to choose a reputable source that follows strict quality control measures. This ensures that you are getting a high-quality product that is free from contaminants and retains its nutritional integrity.
The Nutritional Profile of Bee Pollen
The nutritional profile of bee pollen is truly remarkable. It is a complete protein source, containing all essential amino acids required by the human body. This makes it an excellent supplement for those following a vegetarian or vegan diet. Additionally, the high concentration of vitamins and minerals in bee pollen makes it a valuable addition to any diet.
Vitamins and Minerals in Bee Pollen
Bee pollen contains a broad spectrum of vitamins, including vitamin A, vitamin B complex, vitamin C, and vitamin E. These vitamins play vital roles in various bodily functions, such as supporting the immune system, promoting healthy skin, and aiding in energy production.
Proteins and Amino Acids in Bee Pollen
Proteins are the building blocks of our bodies, and bee pollen is an exceptional source of high-quality protein. It contains all essential amino acids, including those that the body cannot produce on its own. These amino acids are crucial for muscle growth and repair, as well as maintaining overall health.
5 Health Benefits of Bee Pollen
- Nutrient-Rich Superfood: Bee pollen is considered a superfood because it is packed with essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, proteins, and amino acids. It contains B vitamins, vitamin C, vitamin E, and minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, making it a well-rounded source of nutrition.
- Antioxidant Properties: Bee pollen is rich in antioxidants, such as flavonoids and carotenoids. These antioxidants help protect cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals. By reducing oxidative stress, bee pollen may contribute to overall health and longevity.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Some studies suggest that bee pollen has anti-inflammatory properties. This can be beneficial for reducing inflammation in the body, which is linked to various chronic diseases, including heart disease and arthritis.
- Allergy Relief: Contrary to what one might expect, bee pollen has been used by some people to alleviate seasonal allergies. The theory is that small, regular exposures to the pollen can desensitize the immune system and reduce allergy symptoms. However, this is a controversial and unproven use, and some individuals may experience allergic reactions to bee pollen.
- Energy and Vitality: Bee pollen is often promoted as an energy booster and vitality enhancer. Its nutrient content, including proteins and carbohydrates, can provide a natural source of energy. Some people use it to combat fatigue and increase stamina.
How to Incorporate Bee Pollen into Your Diet
Integrating bee pollen into your diet is simple and can add a nutritional boost to your meals. Here are a few ideas on how to incorporate bee pollen:
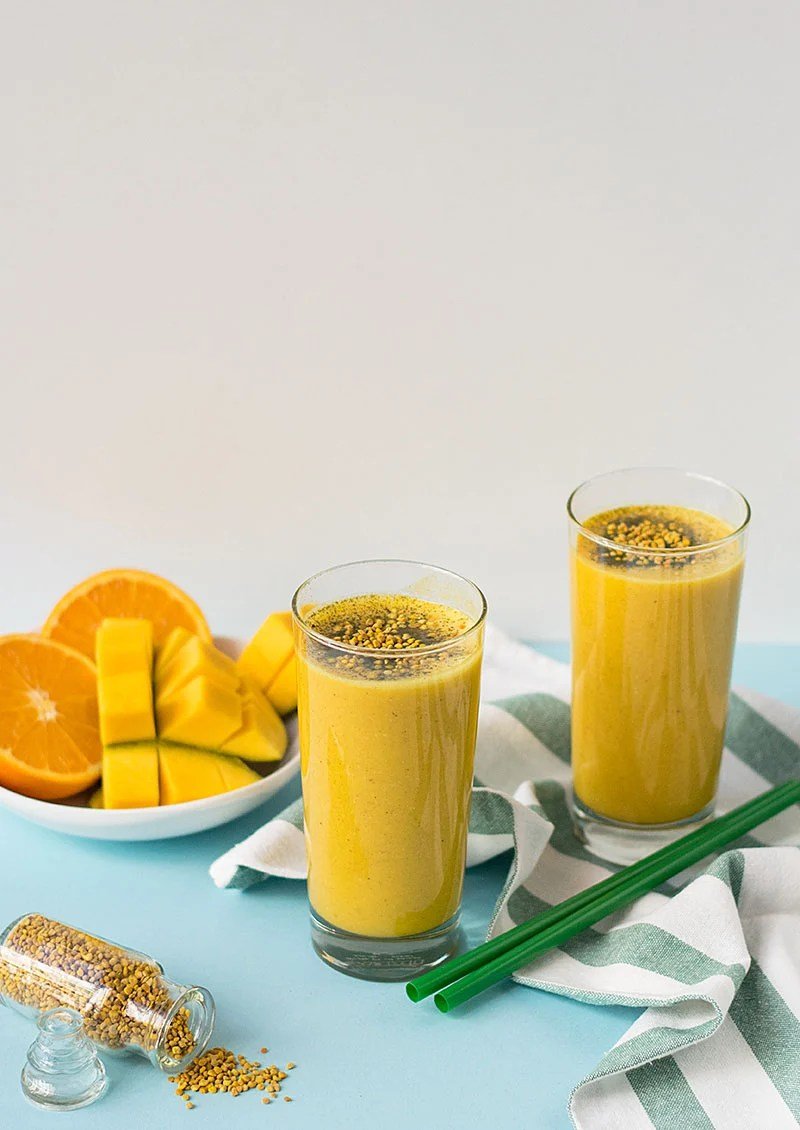
Bee Pollen in Smoothies and Juices
Add a tablespoon of bee pollen to your favorite smoothie or juice blend. This addition will not only enhance the taste but also provide an extra nutritional punch to your beverage.

Cooking with Bee Pollen
Sprinkle bee pollen over salads, cereal, or yogurt for a crunchy and nutritious topping. It can also be used as a flavorful seasoning for various dishes, such as roasted vegetables or grilled meats.
Precautions and Potential Side Effects of Bee Pollen
While bee pollen offers numerous health benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential precautions and side effects.
Allergic Reactions to Bee Pollen
Some individuals may have allergies to bee pollen, especially if they are allergic to bee stings or other bee products. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating bee pollen into your diet if you have known allergies.
Interactions with Medications
Bee pollen may interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners and immunosuppressants. If you take any medications, it’s crucial to discuss with your healthcare provider before starting bee pollen supplementation.